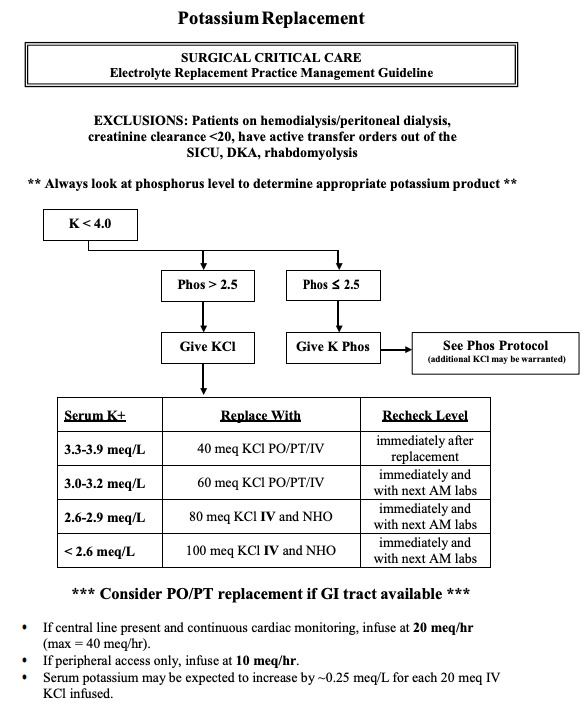
Potassium
- (always check Mg and replete PRIOR to repleting K. Low Mg can worsen K losses)
- Goal serum potassium level: ∼ 4.0 mEq/L
- Expected increase in serum potassium levels: ∼ 0.1 mEq/L after an IV dose of 10 mEq
- Use caution with repletion in patients with impaired renal function.
- Oral uptake can be improved by administration with or after a meal.
- Regular saline is usually preferable to 5% glucose as infusion fluid (to avoid transcellular potassium shift)??
- Adverse effects of potassium repletion
- Hyperkalemia
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- GI upset (PO administration)
Extravasation (IV administration) - Local irritation (IV administration)
Magnesium
- Goal serum magnesium level =2
- In patients with an underlying cardiac disorder and/or at risk of arrhythmias: consider higher goal > 1.7 mg/dL
1 g of IV magnesium sulfate has about 8 mEq of elemental magnesium.
Oral repletion is generally preferred when possible - Magnesium repletion should be continued 1–2 days after normalization of serum levels.
- Adverse effects
- Soft stools, diarrhea
- Nausea, vomiting
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness, attenuation of muscle reflexes
- Low blood pressure
- Impaired respiratory effort, cardiac arrest
- Hypermagnesemia
- In patients with an underlying cardiac disorder and/or at risk of arrhythmias: consider higher goal > 1.7 mg/dL

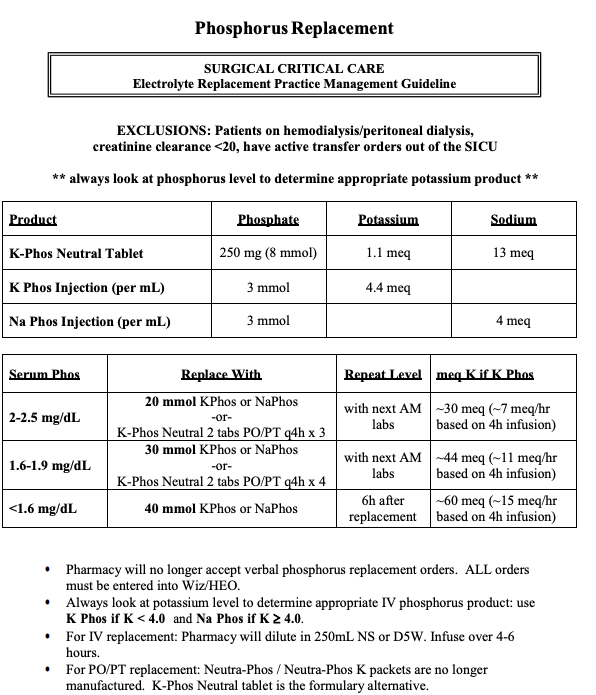
Phosphorus
- Expected increase in serum phosphorus levels: ∼ 0.5 mg/dL with a dose of 0.10 mmol/kg body weight (but this is somewhat unpredictable).
- Adverse effects of phosphate repletion
- Hypocalcemia, hypernatremia
- Osmotic diuresis
- Renal failure
- Arrhythmias
- Confusion, dizziness, seizure, tetany
- Precipitation with calcium (stones)
- Hyperkalemia
- Diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting
- Sore throat
- “Stones (kidney), Bones (n/a – more for PTH which inc bone resorption), Groans (indigestion, n/v, diarrhea, PUD!), Moans (lethargy), Thrones (polyuria or constipation), and Psychiatric Overtones (psych issues)!”
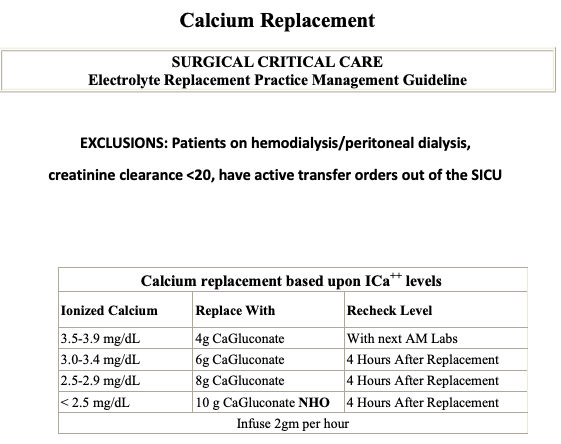
#Calcium
- Goal serum calcium level: low–normal range (e.g., ∼ 8.5 mg/dL)
- The ionized calcium level is the best measure of physiologically active calcium.
- When using serum calcium, make sure to correct for albumin. Ca + Albumin defecit*0.8 = corrected albumin
- Adverse effects of calcium repletion
- Local irritation
- IV extravasation and soft tissue calcifications
- cardiac slowing… Hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac arrest
From: https://www.vumc.org/trauma-and-scc/sites/vumc.org.trauma-and-scc/files/public_files/Manual/Electrolyte%20Replacement.pdf
and Amboss
Zaloga GP, K.R., Bernards WC, Layons AJ, Fluids and Electrolytes. Critical Care, ed. T.R. Civetta JM, Kirby P.Vol. 1. 1997, Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven. 23.63. Panello JE, Delloyer RP, Critical Care Medicine 2nd Edition 2002; St. Louis: Mosby, Inc. 1169 Polderman, et al. CCM 2000 June; 28(6) 2022-2025 Polderman et al. J. Neurology 2001 May; 94(5): 697-705
Leave a Reply